Confectionery – Premium Sweets & Treats
Confectionery is the art of making sweet foods, collectively known as confections. These sugar-rich and carbohydrate-based delights have delighted humankind for centuries, blending culinary creativity with cultural celebration.
In general, confectionery is divided into two overlapping categories:
Baker’s Confectionery (or flour confections): Includes sweet pastries, cakes, and baked desserts — excluding everyday breads.
Sugar Confectionery (or candy making): Includes candies, chocolates, toffees, chewing gums, pastilles, candied nuts, and sugar-free variants.
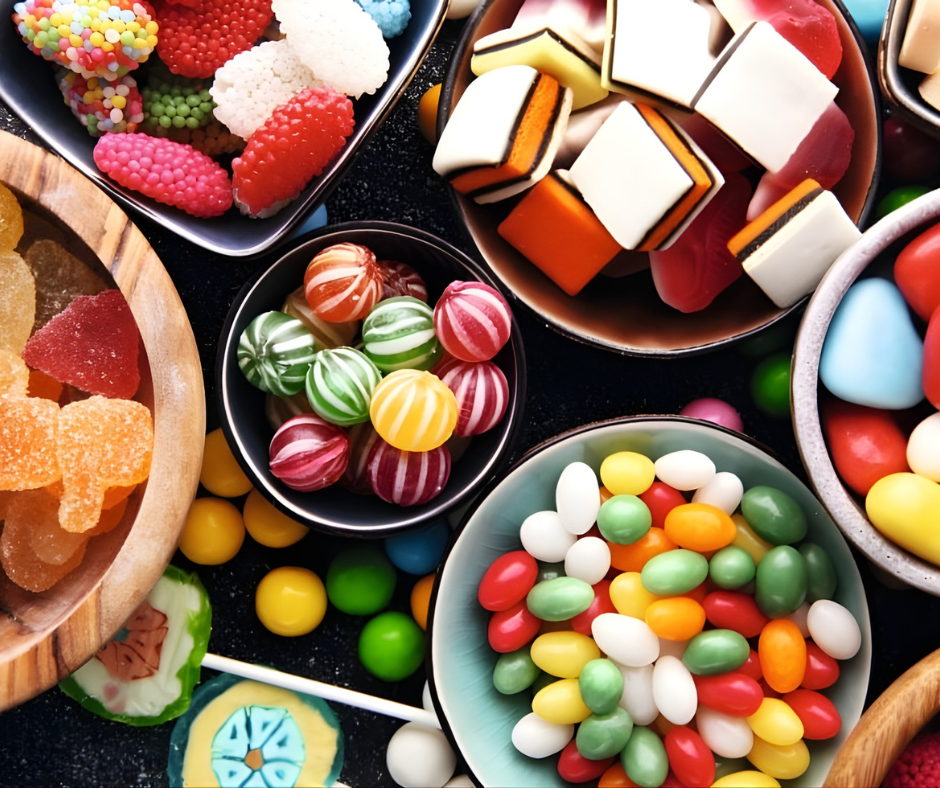

Origin and Identity
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Alternative Name | Sweets / Candy / Chocolates / Sweetmeats |
| Scientific Category | Processed Food (Sugar & Cocoa Derivatives) |
| Description | Edible sweet products made from sugar, cocoa, milk solids, nuts, or fruits, using refined processes for texture and flavor |
| Type | Processed Food / FMCG |
| Primary Ingredients | Sugar, cocoa, milk, nuts, fruits, flavorings |
| Primary Production Regions (India) | Maharashtra, Gujarat, Tamil Nadu, Uttar Pradesh, West Bengal |
| Country of Origin | India |
| Global Recognition | India is one of Asia’s largest producers and exporters of confectionery, supplying to over 120 countries |
| Distinct Features | Diverse taste profiles, long shelf life, attractive packaging, strong domestic and export markets |
| Traditional Roots | Evolved from ancient Indian sweets (mithai), now blended with Western confectionery styles |
Categories of Confectionery
| Type | Examples | Highlights |
|---|---|---|
| Baker’s Confectionery | Pastries, sweet rolls, cakes, cookies | Made from flour and sugar; often baked |
| Sugar Confectionery | Candies, toffees, gums, mints, lollipops | Made mainly from sugar syrup, colorings, and flavorings |
| Chocolate Confectionery | Bars, pralines, coated nuts, truffles | Based on cocoa and milk solids |
| Ethnic Indian Confectionery | Soan papdi, barfi, gajak, toffee burfi | Exported under traditional and fusion brands |
| Functional / Premium Confectionery | Sugar-free, dark chocolate, fortified candies | Rising trend for health-conscious and luxury consumers |
Nutritional Value (per 100 g, average)
Manufacture and Processing
India’s confectionery manufacturing blends traditional craft with automated technology to deliver safe, high-quality sweets for domestic and export markets.
Processing Stages:
Ingredient Preparation: Refining sugar, roasting cocoa beans, preparing syrups.
Cooking & Mixing: Controlled heating and blending to achieve desired texture.
Molding & Shaping: Creating bars, candies, or filled chocolates.
Cooling & Wrapping: Sealing freshness and preventing moisture absorption.
Packaging & Branding: Designed for export shelf life and appeal.
Quality & Compliance:
FSSAI-certified manufacturing units
ISO 22000 & HACCP food safety systems
DGFT & APEDA registration for exports
Labelling under Codex Alimentarius standards for international trade
Export Overview (2024–25)
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| HS Codes | 1704 (Sugar confectionery) / 1806 (Chocolate & cocoa preparations) |
| Estimated Export Value | USD 800 million – 1.1 billion annually |
| Top Importing Countries | USA, UAE, UK, Saudi Arabia, Nepal, Bangladesh, Australia, Singapore |
| Key Export Ports | Mumbai, Mundra, Chennai, Kolkata, Nhava Sheva |
| Regulatory Bodies | APEDA, FIEO, DGFT, IBEF |
Leading Manufacturers and Exporters
1. ITC Ltd.
Founded: 1910
Business Type: Confectionery & Premium Chocolates (Candyman, Fabelle)
Origin: India
2. Parle Products Pvt. Ltd.
Founded: 1929
Business Type: Confectionery & Candy (Melody, Kismi, Mango Bite)
Origin: India
3. Amul
Founded: 1946
Business Type: Milk & Dark Chocolates
Origin: India
4. Haldiram’s
Founded: 1937
Business Type: Indian Sweets & Chocolate-Coated Snacks
Origin: India
Sustainability and Innovation
Promotion of sustainable cocoa cultivation in southern India (Kerala, Karnataka, Tamil Nadu).
Use of eco-friendly & recyclable packaging materials.
Development of sugar-free, vegan, and fortified products.
Government initiatives under PMFME Scheme for MSME confectionery units.
Conclusion
Confectionery is more than a sweet indulgence — it is an art form that unites tradition, technology, and trade. From ancient Indian sweets to modern gourmet chocolates, India’s confectionery industry continues to expand its reach, symbolizing the country’s culinary creativity and export excellence.
With rising global demand, sustainable practices, and premium quality standards, Indian confectionery stands proud as a blend of heritage and innovation, spreading sweetness across the world.